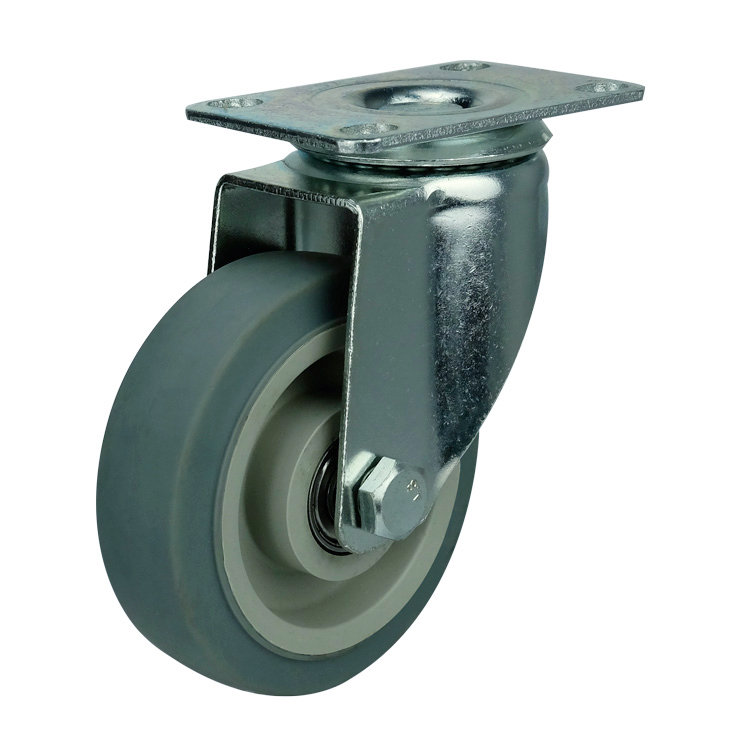
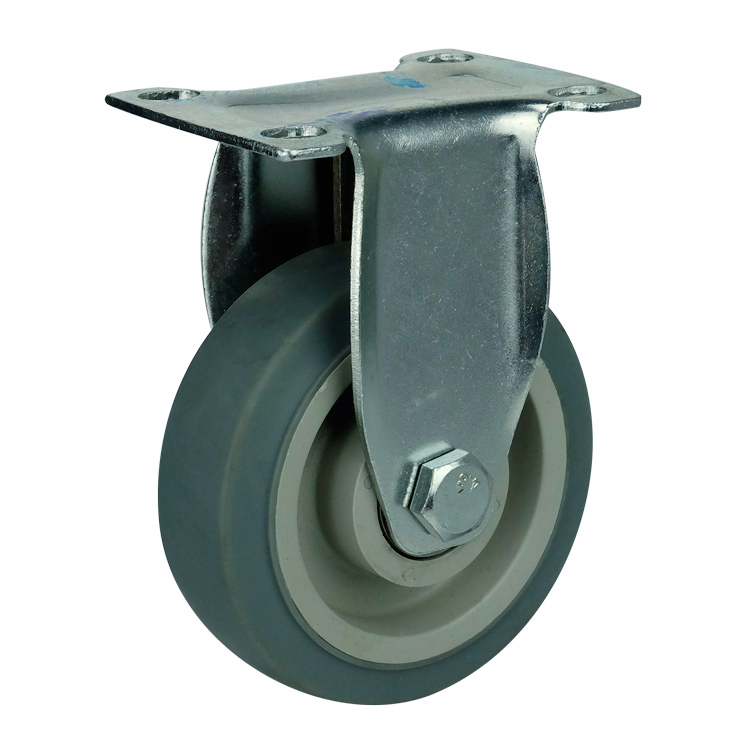
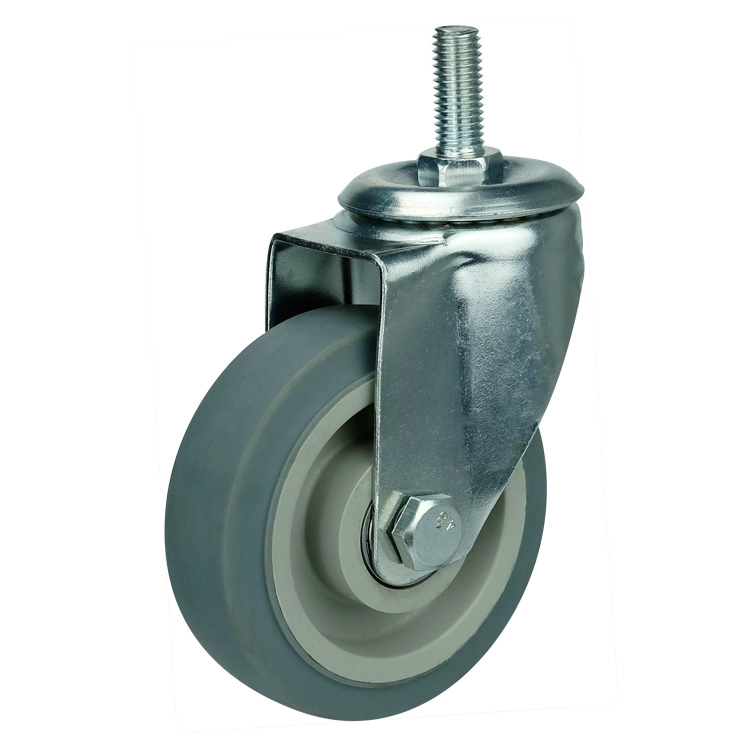
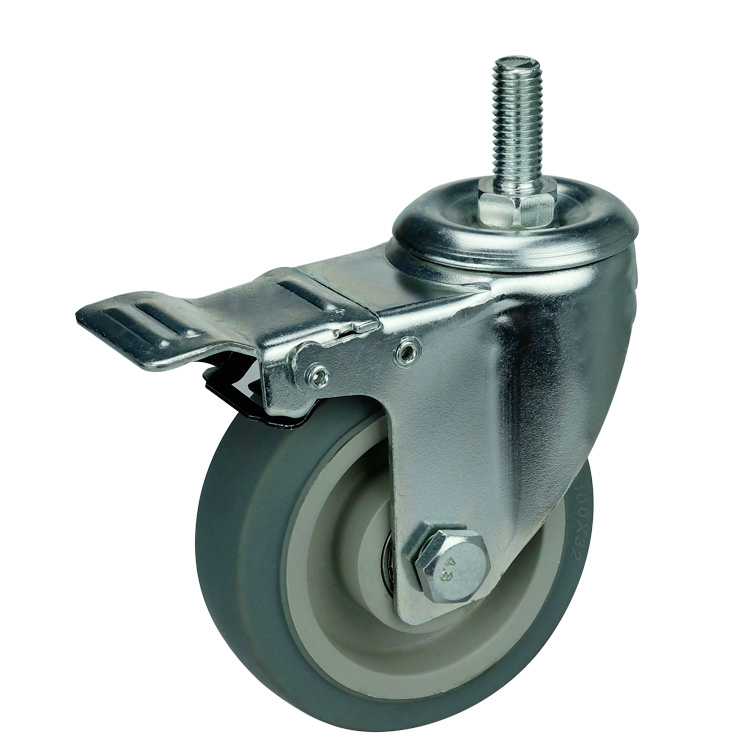
WBD Medium TPR Caster
Characteristics of TPR casters :
Bracket: double ball track and unique anti-steel wrist arc design, more resistant to weight, flexible rotation. It is more practicable. The bracket base plate adopts standard 3mm thick steel plate and the leg material with 2.3mm thick steel plate stamping. Welding forming, surface galvanizing.
Wheel: made of ultra-high strength plastic core package with high strength super synthetic rubber (TPR), highly elastic, which equipped with an integrated precision ball bearing, beautiful and nearly without noise . Besides , it can be very good protection for the floor, suitable for hospital, hotel, car factory assembly workshop (epoxy resin) and other places.
Advantages : Noiseless ; Durable ; Without smell ; With competitive price .
Application : Hospital ; Hotel ; Office and other environment .
Specifications: swivel , fixed, threaded stem , double brake (lock the bracket and wheel).
The wheel diameter: ¢75 mm (3 inch), ¢100 mm (4 inch), ¢125 mm (5 inch).
Our industrial casters are very competitive , have different size : 3 inch casters , 4 inch casters and 5 inch casters
1. Application of shock absorbing caster:
The shock absorbing caster is mainly used in the automotive industry, because of its characteristic of shock absorption performance, it can play a good shock absorption effect. For the shock absorbing wheels, it generally require the caster has good rotation performance and stress performance.
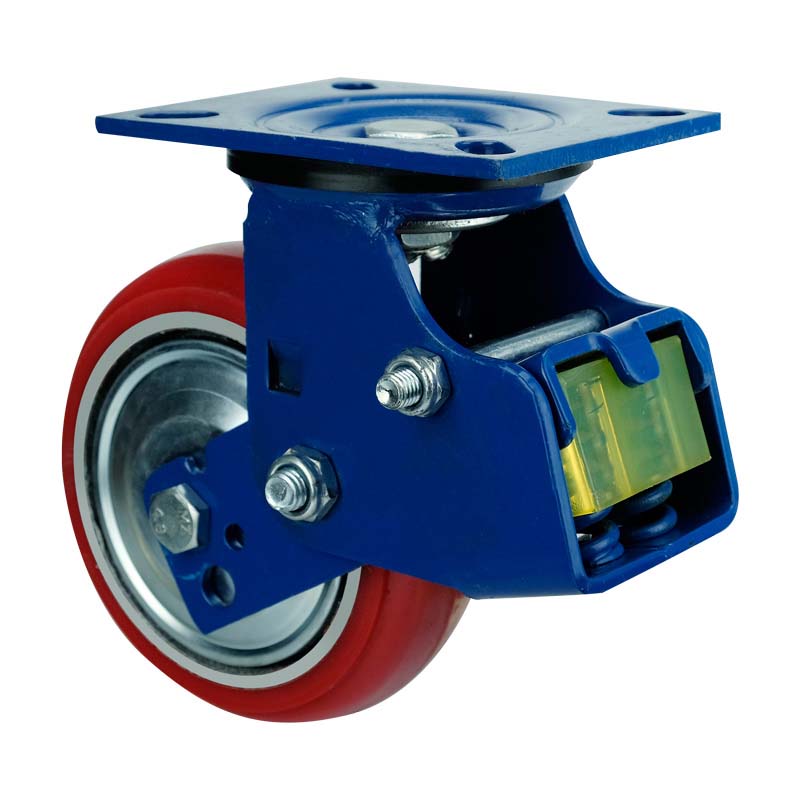

2. Features of Shock Absorbing Casters:
a. Spring:The anti-vibration springs of some models of shock absorbing wheels are completely sealed and with dust-proof and anti-wrap properties. In order to suit different options and requirements. We should choose an excellent shock-resistant and shock-resistant spring to prevent the wheel from being damaged due to vibration when working on uneven ground.
b. Shock performance:
The spring loaded caster is made of high-quality shock-resistant shock springs. By using large-diameter bead disk, and with the top plate and the upper and lower bead plate being heat-treated, it can greatly improve the rigidity and toughness of the bead plate, making the bead plate rotation more flexible and easy, and greatly increasing the force Performance, avoiding the wheel damaged by vibration on the bumpy ground.
c. Resistant to high speed:
Double-tapered roller bearings are used for the spring casters wheels, which can better prevent wheel wobble during high-speed traction and greatly reduce noise, providing a quiet production environment for the production workshop.
d. Selection of Material:
High-quality thermoplastic rubber material wheel, it has good toughness and wear resistance.
High-tech polyurethane-coated iron core wheel its characteristics are antifouling, oil resistance, abrasion resistance and high load bearing.
For more choices, please check below direct links or send us inquiry.
http://www.ylcaster.com/red-pu-spring-loaded-casters_p202.html
http://www.ylcaster.com/polyurethane-heavy-duty-shock-absorbing-casters_p199.html
http://www.ylcaster.com/125-mm-polyurethane-spring-loaded-caster-wheels_p196.html
YL caster team - Heart to heart
Yl caster team ,who provide the Caster Wheelsfor the people that is the traders,the dealers and the agents for castors and wheels.and also the factory which required the heavy duty casters , industry casters, furniture casters and the hospital medical casters ,is a best team.

We work hard together to become a professional casters expert,to provide customers with the most suitable products ,to be a master of caster .


The morning meeting encourage everyone to welcome the brand new day !
We would share the worth things and analysis of cases which anyone of us can not make a deal by himself .
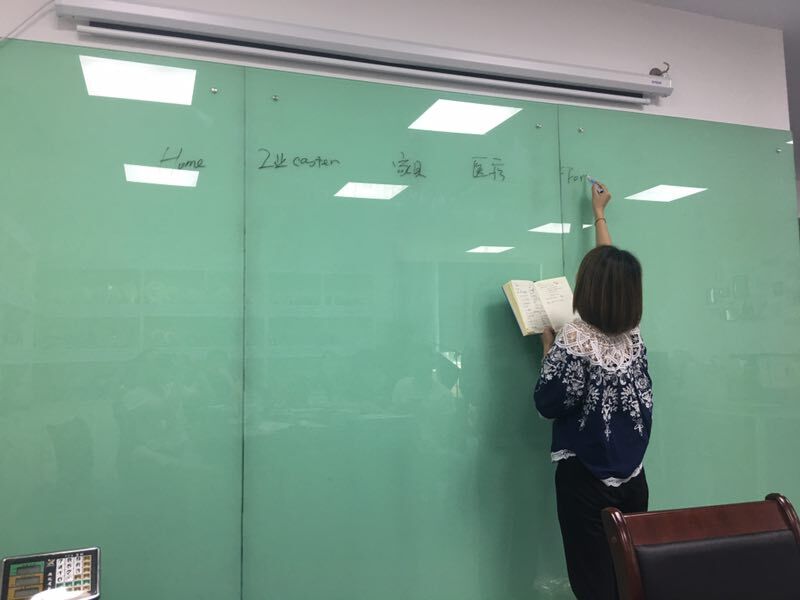

The heart of our company cultural is FAMILIES CULTURAL .
We build the cultural wall together .

Every Wednesday is the day of team building .we have may activities .
Such as Reading together


Study together

Running together

Singing Together
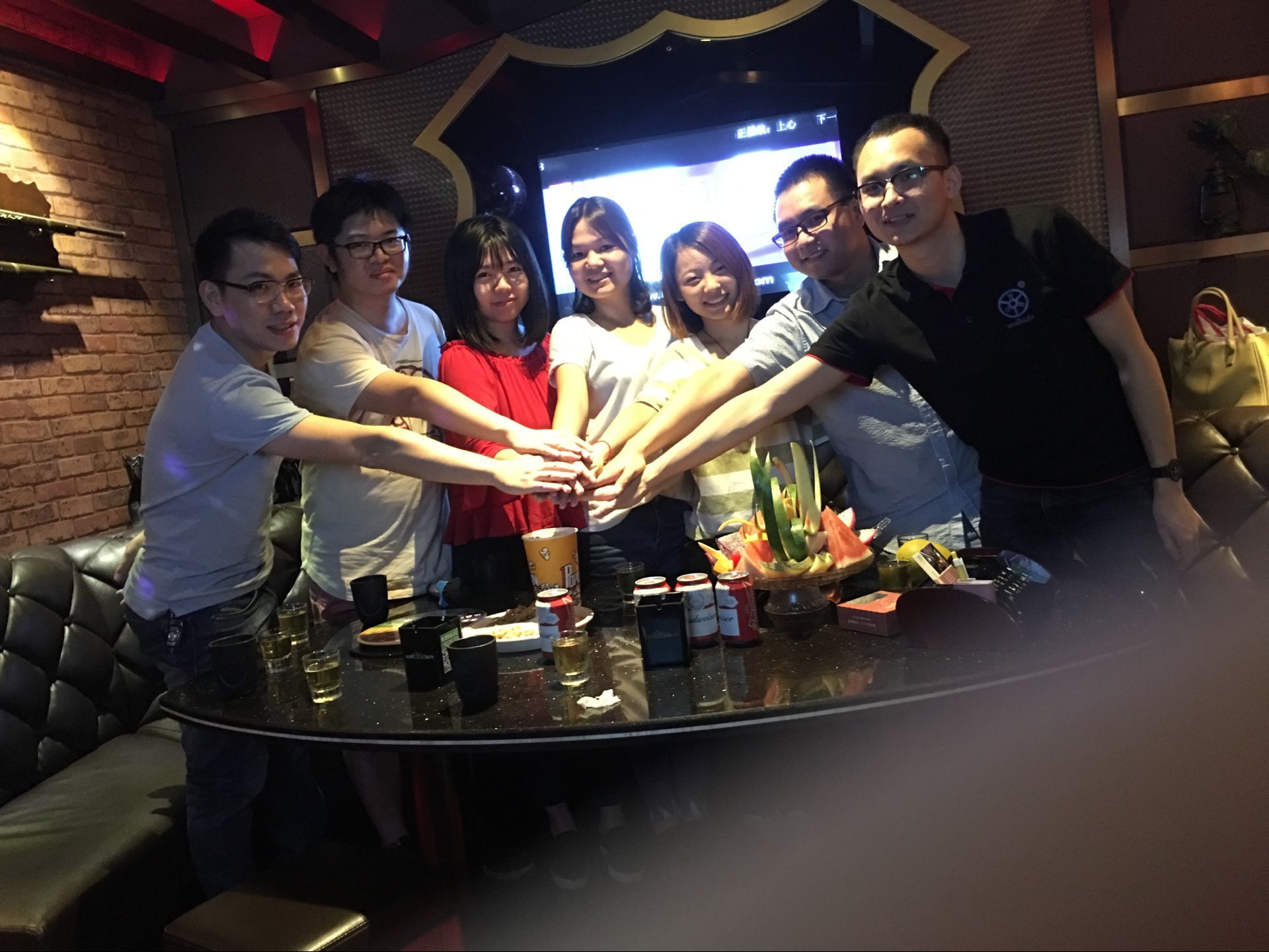
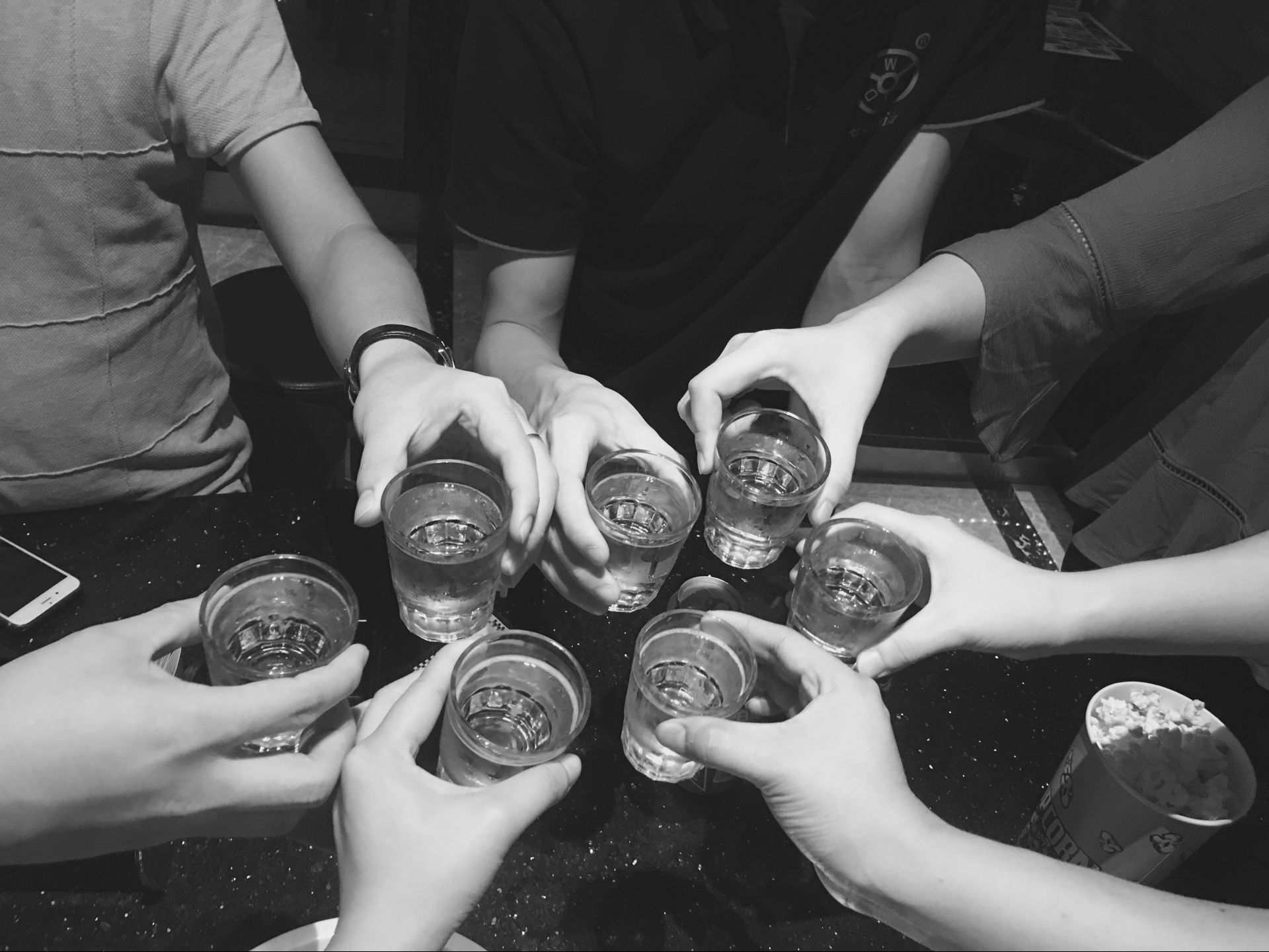


An so on ...
Motivation is not motivate individuals, motivation is to motivate a team. As long as we can dream, we can do it. Heart to heart, we are Guangzhou YL Caster Industry Co., Ltd.
Cast iron casters in today

There are many types of cast iron casters, which are mainly divided by load capactiy level. They can be divided into light duty cast iron casters, medium duty cast iron casters and heavy duty cast iron casters. The applicable range is also very wide. Like heavy duty cast iron casters, due to their strong, wear-resistant, high load-bearing characteristics, they are usually used for handling tools such as industrial trolleys. With the advent of the retro trend, they are now more used on the table, with different surface treatments and colors, used as the legs of the coffee table, coffee table, etc., and even the bed. From industrial casters to furniture casters, the style of painting is completely different.
We YLcaster is a powerful manufacturer specializing in the design, production and sales of various caster wheels. We can provide you with different kinds of cast iron core polyurethane swivel caster. In addition, it also supports various customization of casters. Friends who are interested and in need are welcome to consult and understand.
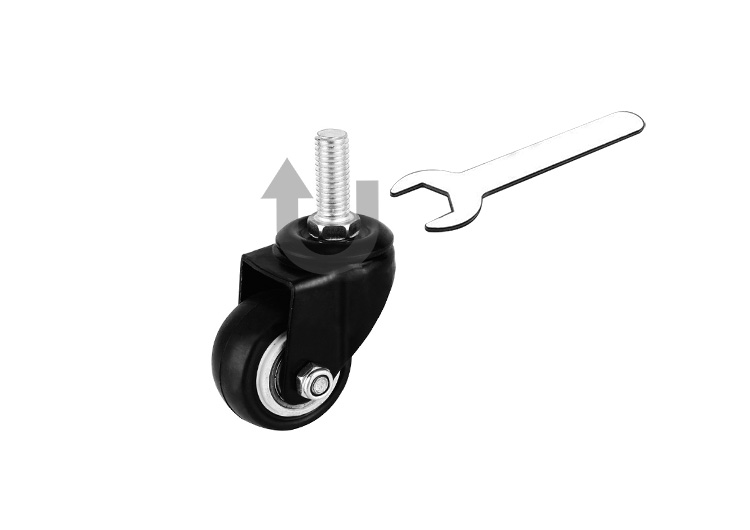
How to install casters with stem
First of all, we need to understand what is a stem caster wheel. The stem is one of the more common ways to install casters. Usually the installed object and the caster are fixedly connected by this rod. Compared with threaded stem and grip ring stem, the installation methods and the structure is simpler. Compared with plate caster wheel, the load-bearing structure is slightly weaker, so it is generally reflected in light duty caster wheel and medium duty caster wheel, which are mainly used in scenes where load-bearing requirements such as furnitures and ordinary platform trolleys are not too large. Of course, for medium duty and heavy duty scenes, the ratio is relatively small.
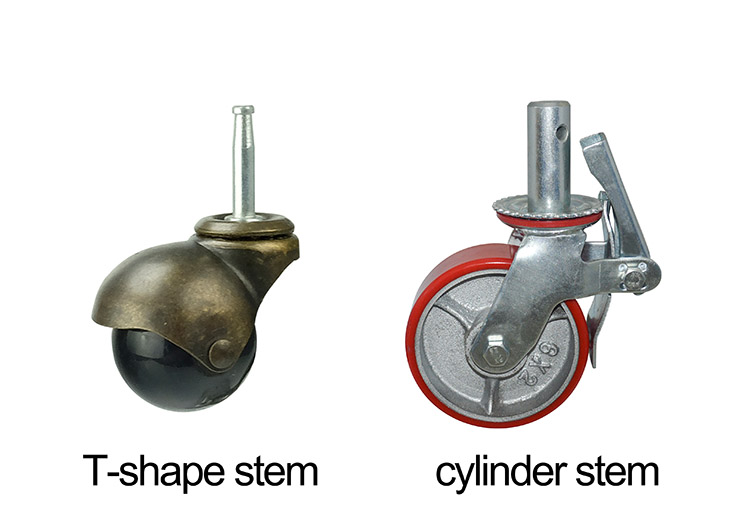
There are two main types of stem casters. One is a thin T-shaped stem, and some are matched with a threaded sleeve; the other is a cylindrical or square column or other polygonal column. The rod usually has a through hole.
So how to install them? The T-shaped stem is the easiest to install, just plug it directly into the set hole of the object to be installed. It's the opposite when removing it, just pull it out. For threaded bushings, plug the bushing into the mounting hole first, and then insert the stem into place. The sleeve and the plunger act like expansion screws at this time to prevent the casters from falling off.
The principle of the inserted stem with holes is similar, except that the upper and lower diameters of the stem are the same size. After inserting in place, you need to insert a pin or other accessories into the through hole for fixing to prevent the caster from falling off when the installed object is off the ground.
T-shaped stem casters are generally smaller than columnar ones. They are usually embodied as furniture casters such as chair caster wheels and table caster wheels. Even with brakes, most of them only stop the wheel from rotating and cannot fix the direction of the caster wheel. Column-shaped stem casters are relatively larger, and are generally embodied in small and medium-sized equipment such as trolley caster wheels, shopping cart caster wheels, and even industrial caster wheels such as scaffold caster wheels, or medical caster wheels. Due to the existence of through-holes and bolts and other accessories, this type of stem casters can usually achieve the function of double brakes, while fixing the direction of the wheel and the caster.
If you have any questions about this or are interested in casters, please feel free to consult. We are specialized in the design, production and sales of caster wheels and hand trolleys-YLcaster.
Threaded stem casters, as the name implies, are casters with threaded stem. The installation method is to connect the screw to the required object by rotating the screw to fix it to the object. Due to the limitation of force, threaded stem are usually used in light duty casters, medium duty casters and other furniture, non-heavy duty industrial appliances, medical equipments, etc.
Generally speaking, the larger the wheel size, the larger the threaded stem diameter, because the load-bearing capacity becomes larger. The length of the threaded stem is determined for the specific use situation. Threaded stem casters are usually also swivel/universal casters, and the wheels themselves can rotate 360degrees under unlimited conditions. Therefore, you cannot hold the caster to install it firmly.
To solve this problem, people invented a threaded stem with a nut. Therefore, you will find that there is usually a nut at the bottom of the threaded stem, which is completely integrated with the threaded stem, unless the threaded stem breaks, avoiding the embarrassment of slipping.
When installing threaded stem casters, we usually use a thin wrench to turn the nut counterclockwise until it can no longer be turned. The threaded stem is tightly combined with the installed object. Of course, some designs themselves are bolt-hole casters, and screw a screw directly from under the hole, which also needs to be tightened by a wrench. There are also designs where the bolt-hole has a locking position, and the screw does not have a nut, but it has a clip. By combining with the hole locking position, it can be fixed by rotating the entire caster.
Compared with top plate casters, threaded stem casters are more convenient to install, only need to screw a nut. However, there are disadvantages, the installation firmness will be smaller than the top plate casters, and the force capacity is also slightly weaker.
Threaded stem casters are mostly reflected in such application scenarios as furniture casters, medical casters, platform trolleys, and shopping carts.
If you have any questions about this or are interested in casters, please feel free to consult. We are specialized in the design, production and sales of caster wheels and hand trolleys-YLcaster.
Impression of the 126th canton fair-WBD(YLcaster)
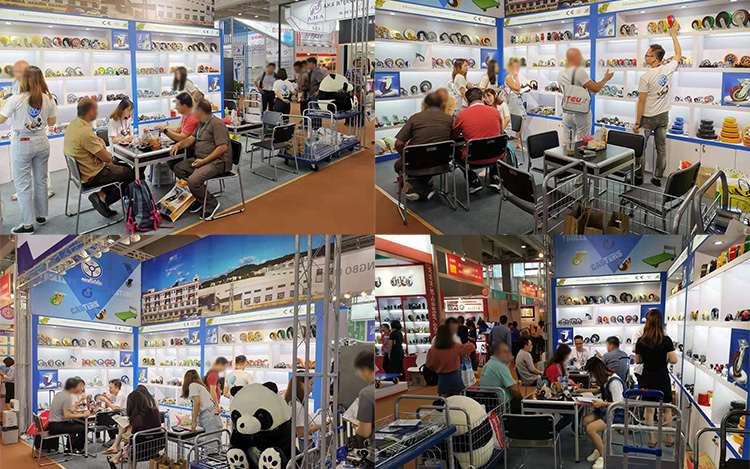

It is the fourth day of the 126th canton fair. During these days, we met a lot of friends who interested in caster and trolley from different countries. We shared informations with each other and builted business relationship. It is a great beginning!
Low temperature affects casters-YLcaster
Now that the northern hemisphere has entered winter, temperatures have generally fallen. Due to the low temperature, many metal products are easily brittle and cracked. Casters are widely used in our lives. Most of the parts and even the entire casters use metal. If the production is not handled properly, the metal parts of the casters will also be damaged.Many fracture accidents occur at low temperatures, especially with steel brackets for casters. This is because temperature has a great influence on the properties of widely used steel and cast iron. As the temperature decreases, the yield strength of steel increases and the toughness decreases. The existence of brittle transition temperature of body-centered cubic metal is one of its brittleness characteristics. As the temperature decreases, the fracture form of the notched impact specimen changes from ductile to brittle fracture within a certain temperature range. This type of fracture transition is usually expressed by a specific transition temperature, which is of a certain significance The above characterizes the material's ability to resist low temperature brittle fracture. This phenomenon that the material changes from toughness to brittleness with decreasing temperature is called low temperature brittleness or cold brittleness, and the temperature at which brittleness transition occurs is called brittle transition temperature.
We-YLcaster, is a company specializing in the design, production and sales of casters, like heavy duty industrial casters, low profile furniture casters, medical wheels casters etc. We will use professional knowledge and experience to select the metal materials required for the manufacture of casters, choose a scientific and reasonable treatment method, and provide products of reliable quality that are not affected by low temperature, which will make customers comfortable.

Recently, a batch of transparent polyurethane wheels officially rolled off the injection line. They will soon be assembled into complete casters and shipped to our customers. This translucent double-ball bearing wheel is mainly used for office chair casters, and some people also use it as a pulley wheel. The wheel sizes are generally 2.5 inches, 3 inches and 4 inches. Usually used for chairs are 2.5 and 3 inches. Excessive wheels will cause the caster's center of gravity to be too high and there is a risk of tipping. Judging from the existing styles, the rollerblade style office chair casters made of this kind of wheels usually use a grip ring stem type mounting bracket, which is very convenient for installation or disassembly.
The casters made of the wheels are soft, silent and traceless, and can protect the floor to the utmost extent. The design of double ball bearing and double race is more durable.
This clear PU chair caster wheel is currently a hot-selling style on Amazon, and is generally sold in sets of 5.
Our company also has a sales plan for this product, with customizable bracket color, logo and outer packaging, which is convenient for friends in need to make personalized customization. At the same time, we can also provide shipment services to provide you with a one-stop comfortable shopping experience.
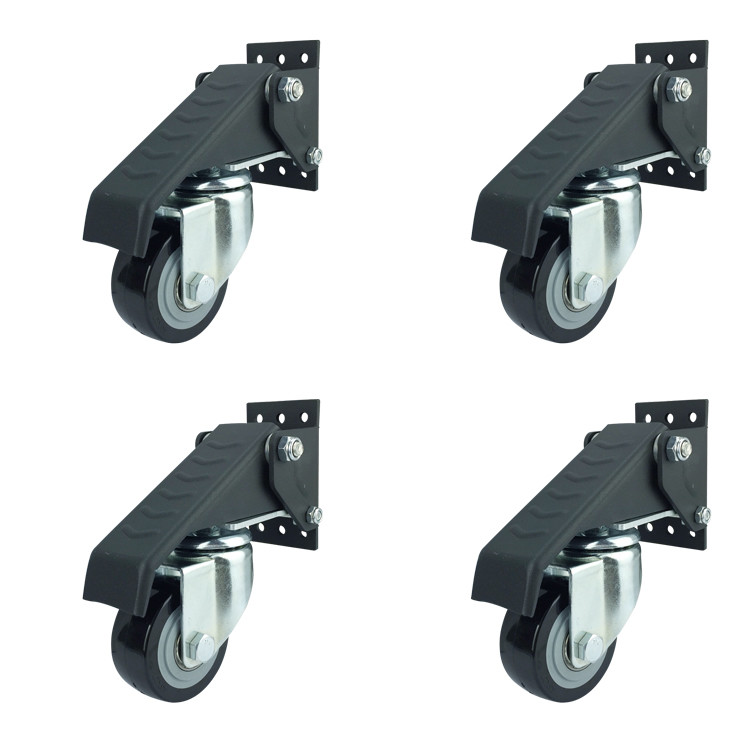
Newest design workbench caster
YLcaster made Workbench Caster 4-pack Set is the perfect solution for easily positioning your heavy workbench to any desired area in your shop. Simply push down on the foot pedals to elevate your workbench off the floor, move to the preferred location, then lift up foot pedal to lower table firmly back onto the floor. Each 60mm polyurethane caster can support 100 lbs. (400 lbs. combined capacity). Experience ease of movement with caster's 360 degrees pivoting action. All mounting hardware included.
Now a great new idea coming out, mounting holes will be increased to 6 screws instead of 2, users can choose the different way they prefer, you can choose center holes to mount while you meet a narrow surface of workbench legs, you can choose 4or 6 holes to make sure enough stability.
One more detail, the pattern for locking fork changes to increase resistance, black wheels made with Polyurethane pressing on the side will also make higher load-bearing, whole black workbench caster and wheels make it looks luxury.
This workbench caster is popular in industrial caster line and furniture market . Please catch this time to contact us .
- Automotive Engine Rubber Parts8
- Automotive Lamps Rubber Parts5
- Automotive Suspension Rubber Parts2
- Automotive Wiring Harness Rubber Parts3
- Extrusion Sealing Strip1
- Industrial Electrical Rubber Parts3
- Industrial Scanners2
- Industrial electrical control3
- Industrial slings4
- Machine Tool Blades1
- Membrane Products1
- Motor1
- Racecource Rubber Products3
- Rubber Forklift Attachments1
- Rubber and plastic Parts1
- Seal2
- Tubular Motor2
- blade1
- brush1
- chip1
- industrial hose1
- lens1
- mold1
- plc3
- pump2
- racking2





