In the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, cleanrooms are key facilities to ensure product quality and safety. One of the core of aseptic technology is to control the laminar air flow speed in the cleanroom to maintain a sterile environment. This article will explore the scientific basis, regulatory requirements and how to combine Class A laminar air flow speed with cleanroom design.
Cleanrooms are designed to control particulate and microbial contamination to protect sensitive manufacturing processes and products. In these controlled environments, air flow is one of the key factors because it directly affects the particle distribution in the air and the removal efficiency of pollutants.
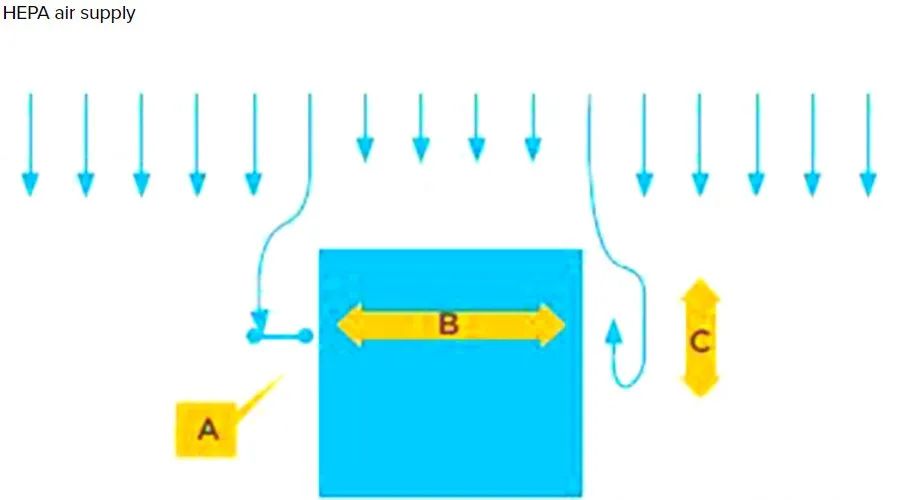
Both EU GMP Annex 1 and NMPA GMP mention that the unidirectional flow system should provide a wind speed of 0.36m/s to 0.54m/s in its working area, but this is only a guide value. This means that in actual operation, as long as it can be scientifically justified, the wind speed can be adjusted according to the specific situation.
EU GMP Annex1:
4.30...Unidirectional airflow systems should provide a homogeneous air speed in a range of 0.36 – 0.54 m/s (guidance value) at the working position, unless otherwise scientifically justified in the CCS. Airflow visualization studies should correlate with the air speed measurement.
Appendix Sterile Drugs Article 9: The unidirectional flow system must deliver air evenly in its working area, with a wind speed of 0.36-0.54m/s (guideline value). There should be data to prove the state of unidirectional flow and be verified. The standard of 0.45m/s±20% actually comes from the US FS 209 standard, which is based on experience and does not consider energy consumption, but more on the noise of the fan. Studies have shown that higher cleanliness can be achieved at lower air speeds because lower wind speeds reduce turbulence around objects in the flow path. When designing a clean room, it is necessary to consider the effect of wind speed on cleanliness. Wind speed not only affects the removal efficiency of particles, but also affects the comfort and energy consumption of operators. When designing, these factors need to be balanced to achieve the best sterile environment.
The regulatory standards for unidirectional airflow velocity in clean rooms vary in terms of measurement location and the weight of a specific velocity. According to the guidance of the US FDA, it is required to measure the airflow velocity at a distance of 6 inches below the filter surface. ISO 14644 requires that the airflow velocity be measured at approximately 150mm to 300mm from the filter surface. However, according to EU (and WHO) GMP, the airflow is measured at the working height, which is defined by the user. Flow velocity and airflow are essentially for the purpose of removing contamination and preventing contamination. The optimal flow velocity can be determined through visualization studies as well as particle monitoring. The purpose of the visualization study is to confirm the smoothness, flow pattern and other spatial and temporal characteristics of the airflow in the device. To this end, the airflow is checked through airflow visualization mapping, by generating smoke and studying the behavior of the smoke, which is then captured with a camera.
Therefore, the Class A laminar air velocity of 0.36m/s to 0.54m/s is not a standard that must be strictly followed, but a guide value. In actual application, the wind speed can be adjusted according to the specific situation. The key is to be able to justify it through scientific methods.
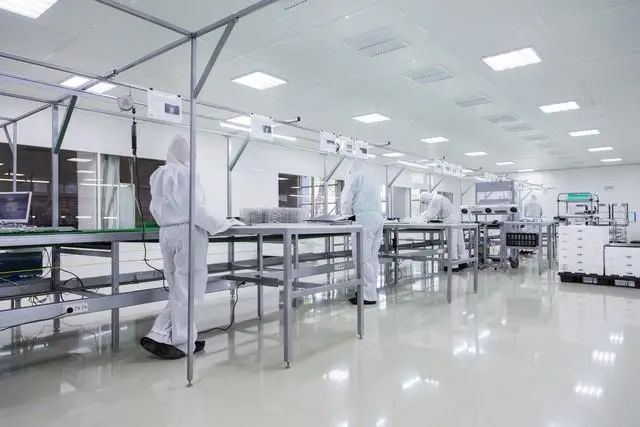

When designing a clean room, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the impact of wind speed on particle control, operator comfort and energy consumption to achieve an optimal sterile environment. Through airflow visualization and particle monitoring, the optimal air speed can be determined to ensure the efficient operation of the clean room, thereby protecting the quality and safety of pharmaceutical products.

Air filtration is an important field in filtration technology and is widely used in many industries and scenarios. Its purpose is to remove fly ash from ambient air, various air inlets, vehicle exhaust, power plant flue gas, and dust particles from incinerator flue gas. Among many filter materials, ePTFE (expanded polytetrafluoroethylene) membrane has become a leader in the field of air filtration due to its unique performance and high efficiency.
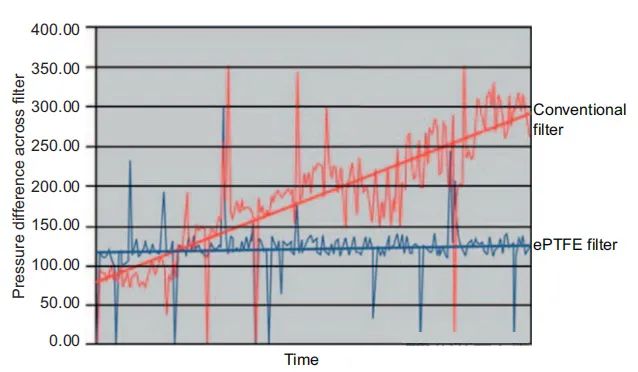
Comparison of pressure difference between ePTFE filter and traditional filter
ePTFE membrane has excellent chemical stability, temperature resistance, low differential pressure and high filtration efficiency. Its microporous structure is very unique, with millions of micropores per square centimeter, and the pore size range is usually between 0.05-0.2μm, which can effectively intercept submicron particles.
The surface filtration mechanism of this material prevents dust particles from entering the filter medium when intercepting them, thus avoiding the common clogging problem of traditional filter media, maintaining a stable pressure difference, and extending the service life of the filter.
The surface filtration technology of the ePTFE membrane enables it to maintain a low pressure drop when intercepting particles, which means that during the air filtration process, the system requires less energy, thereby achieving energy saving. In addition, since the ePTFE membrane does not need to rely on filter cakes to improve filtration efficiency, the filter can be cleaned more effectively, further extending the service life of the filter and reducing maintenance costs.
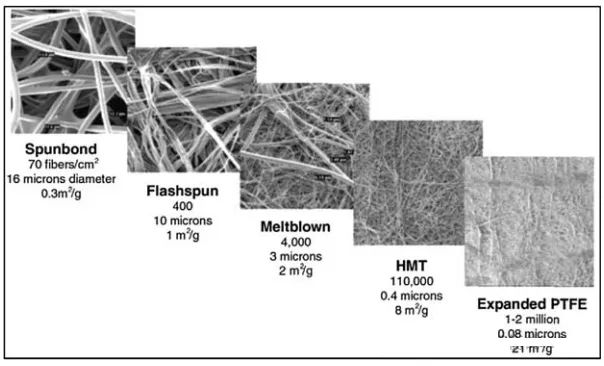
The application of ePTFE membrane in air filtration has demonstrated its excellent performance and broad application prospects. It provides a reliable solution for various air filtration needs through its advantages such as efficient particle interception ability, low pressure drop and long life, and is an indispensable and important material in modern filtration technology.
Activated carbon filters play a vital role in laboratory air purification due to their excellent chemical gas adsorption capacity. They can effectively remove harmful gases, protect the health and safety of laboratory workers, and ensure the accuracy of experimental results. The manufacturing process of activated carbon filters directly affects their performance and reliability, and different manufacturing processes will produce different usage effects and maintenance requirements. This article will explore the manufacturing processes of activated carbon filters in depth, analyze how they affect the performance of the filters, and explore the application of these processes in laboratory air purification. Two Manufacturing Processes of Activated Carbon Filters In the manufacture of activated carbon filters, there are two main processes: granular activated carbon filters
KLC Date: Venue: KLC Booth No: A43 As a leading https://www.klcintl.com/https://www.klcintl.comhttps://www.klcintl.comwww.klcintl.comhttps://www.klcintl.comcompany in the field of air purification systems ✔ Latest product and technology display – Explore KLC's latest research and development achievements in HVAC ✔ On-site expert consultation – Our team will provide you with professional answers and customized solution suggestions ✔ One-on-one business negotiation – We look forward to in-depth exchanges with you to discuss market trends and business cooperation ✔ On-site interactive experience – Some products support on-site demonstrations, allowing you to more intuitively understand their performance and advantages 
Dear friends, We are extremely excited to invite you to visit SEMICON SEA 2025 and explore the cutting-edge technology and unlimited possibilities of the semiconductor industry with KLC Date: Location: Booth: Let us meet at SEMICON SEA 2025 and open a new chapter in the semiconductor industry together! 
Now there are many laboratories are using the air purification program, that is, we often say sterile laboratory, this laboratory generally needs to use the air shower room.
Must the sterile laboratory have an air shower?
Entering the sterile laboratory must be strictly through the air shower flushing channel. Because the human is a huge biological material, therefore, sterile laboratory to implement strict personnel and physical evidence separation." For this reason, in order to prevent contamination from irrelevant personnel entering the laboratory, a set of fingerprint access control system is set at the door of the sterile laboratory. In addition, the floor of the laboratory door is also laid with sticky mat, before entering the laboratory, feet step on the sticky mat can stick to the dust on the shoes and then enter the air shower buffer channel.
Sterile laboratory requirements:
1. The velocity at the air supply outlet in the dressing room and operation room of the purification room is ≥ 0.3m/s, the air speed in the air shower room is ≥ 15m/s, the static pressure difference between the operation room and the environment of the purification room is ≥5Pa, and the system noise is ≤60dB.
2. The second-level (P2) aseptic room is 10,000 grade and local 100 grade, which conforms to the current universal American federal 209E standard.
3. The secondary asepsis room includes high, medium and primary effect filter system, small central air conditioning system, laminar air supply and well return air. The body automatic induction system is adopted in the dressing room and air shower room.
4. In addition to the characteristics of the secondary aseptic room, the third-level (P3) aseptic laboratory also specially sets up electronic interlocking doors, interlocking of transfer Windows and doors, epoxy resin self-leveling ground and water disinfection facilities.
5. The secondary biosafety cabinet is configured. The laboratory and buffer room are both negative pressure Spaces. The relative pressure of the experiment room is -30Pa to -40Pa, and the relative pressure of the buffer room of the purification room is -15Pa to -20Pa.
The role of the air shower in the laboratory:
The main purpose of using the air shower is to ensure the isolation of the laboratory and the outside world. Air shower room can effectively solve the laboratory buffer scheme: air shower room is one of the best purification equipment into the laboratory buffer. It uses high-speed air to blow off and remove particles attached to the surface of clothing or materials. Prevent the staff to bring hair, dust, bacteria into the laboratory, to meet the strict dust-free purification standards of the work site.
The fresh air system is a device that sends fresh outdoor air into the room after filtering through an air supply device. Its core function is to ensure the oxygen content and cleanliness of the indoor air. The high efficiency of the fresh air system is inseparable from its advanced purification technology. The following are six common fresh air system purification technologies:
HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air Filter) is a widely recognized high-efficiency filter material. It is composed of multiple layers of continuously folded sub-glass fiber membranes and is usually used in air purifiers. The surface area of the HEPA filter is large, and when unfolded, it increases by dozens of times compared to when folded, so the filtration efficiency is very outstanding. Its purification principle is based on the principle of particle inertia and diffusion, and can effectively intercept tiny particles in the air, such as dust, pollen, bacteria, etc.
Electrostatic dust collection technology uses the principle of high-voltage electrostatic adsorption to filter pollutants in the air. It uses the high-voltage strong electric field to adsorb particles on the negative or positive plates, and uses the principle of mutual attraction between different charges to achieve purification. This technology is widely used in indoor air purifiers and can effectively remove large particle pollutants in the air.
Activated carbon is divided into three types: coconut shell, fruit shell and coal. Coconut shell activated carbon has the strongest adsorption capacity. The porous structure and large specific surface area of activated carbon enable it to adsorb small particles in the air, such as odors, chemical gases, etc. Its purification principle is to use the physical adsorption of activated carbon to adsorb harmful substances on the surface of activated carbon.
Negative ion technology generates a large amount of negative ions, also known as negative oxygen ions, through a negative ion generator. Negative ions have the functions of sedation, hypnosis, analgesia, increasing appetite, and lowering blood pressure. After a thunderstorm, people feel happy because of the increase in negative ions in the air. Negative ions can reduce pollutants, nitrogen oxides, active oxygen produced by cigarettes in the atmosphere, etc., reducing the harm of harmful substances to the human body. In addition, negative ions can neutralize positively charged airborne dust and make it settle, thereby purifying the air.
Ozone is a strong oxidant, and its purification principle is based on its strong oxidizing property. Ozone can oxidize organic matter, odor molecules and the functional structure of microorganisms in the air, making them inactive, thereby achieving the effect of sterilization and deodorization. This technology is widely used in air purifiers and can effectively remove odors and bacteria in the air.
Photocatalyst technology is a technology that uses new composite nano high-tech functional materials. Photocatalysts (such as titanium dioxide) can produce catalytic effects under ultraviolet light, exciting surrounding oxygen and water molecules into highly active free radicals. These free radicals can decompose harmful organic substances and some inorganic substances in the air, thereby purifying the air. Photocatalyst technology requires ultraviolet light to work, so you need to pay attention to the configuration of the light source when using it.
The fresh air system can effectively remove pollutants from the air and ensure the cleanliness and safety of indoor air through a variety of advanced purification technologies. HEPA high-efficiency filtration technology, electrostatic dust collection technology, activated carbon adsorption technology, negative ion technology, ozone sterilization and deodorization technology and photocatalytic decomposition technology each have their own advantages, which together constitute the powerful purification ability of the fresh air system.
Choosing a suitable fresh air system can effectively improve indoor air quality and create a healthy and comfortable living environment for people.
As a vital part of the medical field, the design of the air supply system of the clean operating room is directly related to the safety and efficiency of the operation. However, the existing air supply devices have some obvious limitations, including insufficient anti-interference ability and difficulty in meeting the personalized needs of doctors and patients for environmental temperature and humidity. In response to these problems, there is an innovative air supply solution-wide-mouth low-speed air curtain different temperature and speed air supply system.
Analysis of existing problems
Currently, the laminar air supply device of the clean operating room faces two major challenges in practical application:
Although the laminar air supply device of the clean operating room is originally designed to create a sterile environment, it is often discounted due to the interference of the surrounding airflow. This interference not only weakens the scope of the clean area, but also affects the ability of the surgical area to maintain a sterile state, which is a problem that cannot be ignored for surgical environments that require extremely high cleaning standards.
On the other hand, the air supply system of the operating room often adopts a unified temperature and humidity setting, lacking the ability to adjust it in a personalized manner. This "one-size-fits-all" air supply method cannot take into account the diverse needs of surgical staff and patients for environmental comfort, especially in temperature and humidity sensitive surgeries, which may have an adverse effect on surgical results and patient recovery.
Limitations of traditional countermeasures
In order to resist the intrusion of external airflow, one of the traditional solutions is to add enclosures around the air supply device. This design can block the surrounding airflow to a certain extent and protect the purity of laminar air supply. However, this method is not perfect. Too high enclosures may hinder the operation of the surgical team and affect the smoothness and efficiency of the operation.
Another traditional countermeasure is to use high-speed air curtains to reinforce the air supply airflow in order to improve its anti-interference ability. Although this can stabilize the air supply to a certain extent, the high-speed airflow may cause discomfort to the personnel in the operating room, especially in operations that require delicate operations. Excessive wind speed may interfere with the surgical process and even affect the results of the operation.
Proposal of innovative solutions
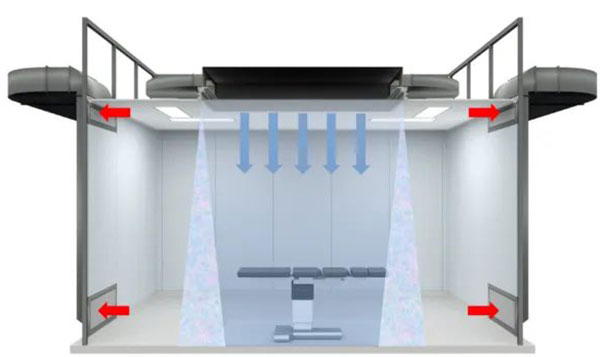
Based on an in-depth analysis of the limitations of the existing clean operating room air supply system, an innovative and breakthrough air supply system design solution is proposed.
This system cleverly arranges three independent and collaborative air supply boxes directly above the operating table. The central box plays the role of main laminar air supply, focusing on providing warm and low-speed clean air to the surgical area to ensure the sterility of the surgical site.
The boxes on both sides are equipped with wide-mouth low-speed air curtain air supply devices, which create a comfortable working environment for surgical personnel with lower temperature and humidity and higher wind speed. This ingenious design of different temperatures and speeds not only significantly improves the anti-interference ability of the air supply system, but also more finely regulates the microenvironment of the surgical space, meets the personalized needs of the surgical site and surgical personnel for temperature and humidity, and thus provides a strong guarantee for the smooth progress of the operation.
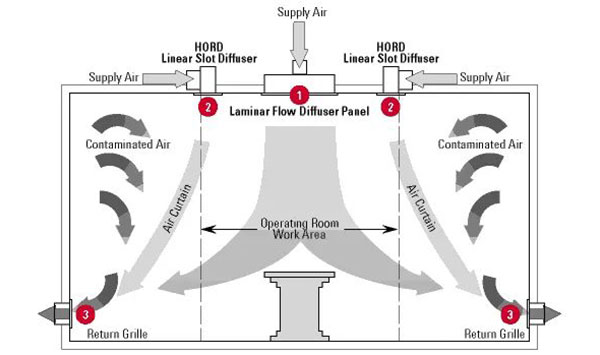
The middle box of the new air supply system is responsible for providing circulating air with higher temperature and lower wind speed to form a sterile and dust-free local environment, while taking into account the comfort of the anesthesiologist. The air curtain air supply devices on both sides provide clean air with lower temperature and higher wind speed to meet the dynamic needs of surgical personnel and effectively eliminate dust and bacteria during the operation.
In addition, the system also achieves precise control of the air supply temperature by configuring different air handling units to meet the needs of different types of surgeries. For example, in cardiac surgery or brain surgery, the system can quickly adjust the air supply temperature to meet the strict requirements of temperature changes during surgery.
The wide-mouth low-speed air curtain variable temperature and variable speed air supply system is not only innovative in technology, but also has significant advantages in practical applications.
It improves the cleanliness of the operating room and the comfort of the surgical staff by optimizing the structure and air supply mode of the air supply device, while reducing energy consumption, which helps promote the sustainable development of the medical industry.
Today we will further share the application of fiber materials, especially cellulose fibers, in air filters. These filters are not only vital in the aviation field, but also play a key role in the automotive industry. They are responsible for removing pollutants from the air, protecting passenger health and improving engine efficiency.
The selection and application of fiber materials directly affect the performance and environmental impact of the filter. Here is a detailed analysis of how these materials achieve a balance between environmental protection and durability in air filtration technology.
Cellulose fibers: ideal for air filters
Cellulose fibers are ideal for manufacturing air filters due to their excellent processing performance, ideal chemical and mechanical properties and low cost.

These fibers can be selected from a variety of materials, including cellulose, thermoplastics and glass fibers, which together form the basis of fuel filters, cabin air filters, engine oil filters and engine air filter paper in automobiles and aircraft.
Bio-based cellulose: an environmentally friendly solution for air filtration

As a bio-based material, cellulose fibers are derived from a natural polymer - cellulose, which is a structural component of plant cell walls.
The bio-based nature of this material means that if the production process is correct, their environmental impact may be less than that of petrochemical-based products such as polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polypropylene (PP). In addition, cellulose fibers are biodegradable and can be broken down by microorganisms into water and carbon dioxide over a certain period of time, which is particularly important for reducing the environmental footprint of air filters.
Regenerated cellulose filter paper: a new choice for air filtration
Regenerated cellulose filter papers are slightly lower than new paper in burst resistance, stiffness and tensile index, but they are still suitable for some undemanding applications. In air filters, this material can reduce the demand for new resources while reducing waste generation.
Although it is not yet widely commercialized, the application potential of regenerated cellulose filter paper in the field of air filtration cannot be ignored.
Application of cellulose fibers in air filters
Although cellulose fibers have the advantages of being bio-based and biodegradable, they often need to be combined with other materials such as chemical fibers and glass fibers to improve durability and reliability in harsh environments. This is particularly important for air filters, as they need to maintain performance under a variety of temperature and humidity conditions.
Companies such as Ahlstrom have developed a series of patented technologies to produce self-sustaining pleated oil media with higher burst strength, which can also be applied to the manufacture of air filters.
After understanding the multifaceted applications and future development of cellulose fibers in air filtration technology, KLC will continue to deepen its air purification technology and continuously explore and develop more efficient and environmentally friendly air filtration solutions.
We are committed to applying the latest fiber technology to the innovation of air filters to meet the growing global demand for clean air and contribute to protecting our environment. With the continuous advancement of technology, we look forward to bringing more breakthrough results to the field of air purification in the future.
- Automotive Engine Rubber Parts8
- Automotive Lamps Rubber Parts5
- Automotive Suspension Rubber Parts2
- Automotive Wiring Harness Rubber Parts3
- Extrusion Sealing Strip1
- Industrial Electrical Rubber Parts3
- Industrial Scanners2
- Industrial electrical control3
- Industrial slings4
- Machine Tool Blades1
- Membrane Products1
- Motor1
- Racecource Rubber Products3
- Rubber Forklift Attachments1
- Rubber and plastic Parts1
- Seal2
- Tubular Motor2
- blade1
- brush1
- chip1
- industrial hose1
- lens1
- mold1
- plc3
- pump2
- racking2